3,4-dihydroxybenzoate
Product of hydrolysis of alyl-3,4-dihydroxybenzic ester. Protocatechuic acid (3, 4-dihydroxybenzoic acid) is a natural phenolic compound found in many edible and medicinal plants.
General
Type : Benzoate
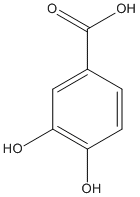
Chemical_Nomenclature : 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid
Canonical SMILES : C1=CC(=C(C=C1C(=O)O)O)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C7H6O4\/c8-5-2-1-4(7(10)11)3-6(5)9\/h1-3,8-9H,(H,10,11)
InChIKey : YQUVCSBJEUQKSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Other name(s) : Protocatechuic acid,4-Carboxy-1,2-dihydroxybenzene,Protocatehuic acid,Benzoic acid, 3,4-dihydroxy-
MW : 154.12
Formula : C7H6O4
CAS_number : 99-50-3
PubChem : 72
UniChem : YQUVCSBJEUQKSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate ligand of proteins in family: Tannase_Bact
Stucture : 4J0J tannin acyl hydrolase in complex with ethyl 3,5-dihydroxybenzoate
Protein : lacpl-tanL
References (5)
| Title : Alterations of Na+\/K+-ATPase, cholinergic and antioxidant enzymes activity by protocatechuic acid in cadmium-induced neurotoxicity and oxidative stress in Wistar rats - Adefegha_2016_Biomed.Pharmacother_83_559 |
| Author(s) : Adefegha SA , Oboh G , Omojokun OS , Adefegha OM |
| Ref : Biomed Pharmacother , 83 :559 , 2016 |
| Abstract : Adefegha_2016_Biomed.Pharmacother_83_559 |
| ESTHER : Adefegha_2016_Biomed.Pharmacother_83_559 |
| PubMedSearch : Adefegha_2016_Biomed.Pharmacother_83_559 |
| PubMedID: 27454871 |
| Title : Crystal structure of tannase from lactobacillusplantarum - Ren_2013_J.Mol.Biol_425_2737 |
| Author(s) : Ren B , Wu M , Wang Q , Peng X , Wen H , McKinstry WJ , Chen Q |
| Ref : Journal of Molecular Biology , 425 :2737 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Ren_2013_J.Mol.Biol_425_2737 |
| ESTHER : Ren_2013_J.Mol.Biol_425_2737 |
| PubMedSearch : Ren_2013_J.Mol.Biol_425_2737 |
| PubMedID: 23648840 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: lacpl-tanL |
| Title : Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of tannase from Lactobacillus plantarum. - Wu_2013_Acta.Crystallogr.Sect.F.Struct.Biol.Cryst.Commun_69_456 |
| Author(s) : Wu M , Peng X , Wen H , Wang Q , Chen Q , McKinstry WJ , Ren B |
| Ref : Acta Crystallographica Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun , 69 :456 , 2013 |
| Abstract : Wu_2013_Acta.Crystallogr.Sect.F.Struct.Biol.Cryst.Commun_69_456 |
| ESTHER : Wu_2013_Acta.Crystallogr.Sect.F.Struct.Biol.Cryst.Commun_69_456 |
| PubMedSearch : Wu_2013_Acta.Crystallogr.Sect.F.Struct.Biol.Cryst.Commun_69_456 |
| PubMedID: 23545659 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: lacpl-tanL |
| Title : Effect of methanol extract of Zanthoxylum piperitum leaves and of its compound, protocatechuic acid, on hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes and lipid peroxidation in rats - Hur_2003_Biosci.Biotechnol.Biochem_67_945 |
| Author(s) : Hur JM , Park JG , Yang KH , Park JC , Park JR , Chun SS , Choi JS , Choi JW |
| Ref : Biosci Biotechnol Biochem , 67 :945 , 2003 |
| Abstract : Hur_2003_Biosci.Biotechnol.Biochem_67_945 |
| ESTHER : Hur_2003_Biosci.Biotechnol.Biochem_67_945 |
| PubMedSearch : Hur_2003_Biosci.Biotechnol.Biochem_67_945 |
| PubMedID: 12834269 |
| Title : Characterization of the protocatechuic acid catabolic gene cluster from Streptomyces sp. strain 2065 - Iwagami_2000_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_66_1499 |
| Author(s) : Iwagami SG , Yang K , Davies J |
| Ref : Applied Environmental Microbiology , 66 :1499 , 2000 |
| Abstract : Iwagami_2000_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_66_1499 |
| ESTHER : Iwagami_2000_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_66_1499 |
| PubMedSearch : Iwagami_2000_Appl.Environ.Microbiol_66_1499 |
| PubMedID: 10742233 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: strsp-PCAL |