Monocrotophos
Insecticide that inhibits monoamine oxidase and acetylcholinesterase. It has been shown to be genotoxic. It was also found to bind a non alpha/beta hydrolase and a not serine hydrolase: Lysozyme (structure 4TUN) 2157-98-4 (for mixed isomers)
General
Type : Organophosphate,Insecticide
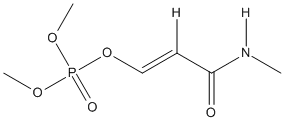
Chemical_Nomenclature : dimethyl [(E)-4-(methylamino)-4-oxobut-2-en-2-yl] phosphate
Canonical SMILES : CC(=CC(=O)NC)OP(=O)(OC)OC
InChI : InChI=1S\/C7H14NO5P\/c1-6(5-7(9)8-2)13-14(10,11-3)12-4\/h5H,1-4H3,(H,8,9)\/b6-5+
InChIKey : KRTSDMXIXPKRQR-AATRIKPKSA-N
Other name(s) : (E)-phosphoric acid dimethyl [1-methyl-3-(methylamino)-3-oxo-1propenyl]ester,dimethyl (E)-1-methyl-2-(methylcarbamoyl)vinyl phosphate,3-dimethoxyphosphinoyloxy-N-methylisocrotonamide,Trade names for products containing monocrotophos include Azodrin, Bilobran, Crisodrin, Monocil 40, Monocron, Nuvacron, Pillardrin, and Plantdrin
MW : 223.16
Formula : C7H14NO5P
CAS_number : 2157-98-4 (mixed isomers) || 6923-22-4
PubChem : 5371562
UniChem : KRTSDMXIXPKRQR-AATRIKPKSA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia : Monocrotophos
Target
References (6)
| Title : Estimation of Monocrotophos renal elimination half-life in humans - Jose_2015_Clin.Toxicol.(Phila)_53_629 |
| Author(s) : Jose A , Selvakumar R , Peter JV , Karthik G , Fleming DH , Fleming JJ |
| Ref : Clinical Toxicology (Phila) , 53 :629 , 2015 |
| Abstract : Jose_2015_Clin.Toxicol.(Phila)_53_629 |
| ESTHER : Jose_2015_Clin.Toxicol.(Phila)_53_629 |
| PubMedSearch : Jose_2015_Clin.Toxicol.(Phila)_53_629 |
| PubMedID: 26065438 |
| Title : Effects of the organophosphate insecticide, monocrotophos, on acetylcholinesterase activity in the nile tilapia fish (Oreochromis niloticus) brain - Thangnipon_1995_Neurochem.Res_20_587 |
| Author(s) : Thangnipon W , Luangpaiboon P , Chinabut S |
| Ref : Neurochemical Research , 20 :587 , 1995 |
| Abstract : Thangnipon_1995_Neurochem.Res_20_587 |
| ESTHER : Thangnipon_1995_Neurochem.Res_20_587 |
| PubMedSearch : Thangnipon_1995_Neurochem.Res_20_587 |
| PubMedID: 7643964 |
| Title : Species differences in brain acetylcholinesterase and neuropathic target esterase response to monocrotophos - Siddiqui_1988_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_23_291 |
| Author(s) : Siddiqui MK , Rahman MF , Mahboob M , Anjum F , Mustafa M |
| Ref : J Environ Sci Health [B] , 23 :291 , 1988 |
| Abstract : Siddiqui_1988_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_23_291 |
| ESTHER : Siddiqui_1988_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_23_291 |
| PubMedSearch : Siddiqui_1988_J.Environ.Sci.Health.[B]_23_291 |
| PubMedID: 3403919 |
| Title : Susceptibility of laboratory-reared northern fowl mites, Ornithonyssus sylviarum (Acari: Macronyssidae), to selected acaricides - Crystal_1988_Exp.Appl.Acarol_4_353 |
| Author(s) : Crystal MM , DeMilo AB |
| Ref : Exp Appl Acarol , 4 :353 , 1988 |
| Abstract : Crystal_1988_Exp.Appl.Acarol_4_353 |
| ESTHER : Crystal_1988_Exp.Appl.Acarol_4_353 |
| PubMedSearch : Crystal_1988_Exp.Appl.Acarol_4_353 |
| PubMedID: 3168660 |
| Title : Incipient cholinesterase inhibition in volunteers ingesting monocrotophos or mevinphos for one month - |
| Author(s) : Verberk MM |
| Ref : Toxicol Appl Pharmacol , 42 :345 , 1977 |
| PubMedID: 595013 |