Naproxen
General
Type : Drug, Naphthalen
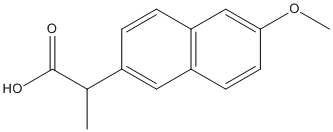
Chemical_Nomenclature : (2S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoic acid
Canonical SMILES : CC(C1=CC2=C(C=C1)C=C(C=C2)OC)C(=O)O
InChI : InChI=1S\/C14H14O3\/c1-9(14(15)16)10-3-4-12-8-13(17-2)6-5-11(12)7-10\/h3-9H,1-2H3,(H,15,16)\/t9-\/m0\/s1
InChIKey : CMWTZPSULFXXJA-VIFPVBQESA-N
Other name(s) : (S)-Naproxen || (+)-Naproxen || Naprosyn || CHEBI:7476 || CHEMBL154 || SCHEMBL3046 || ZINC105216 || DB00788
MW : 230.26
Formula : C14H14O3
CAS_number : 22204-53-1
UniChem : CMWTZPSULFXXJA-VIFPVBQESA-N
IUPHAR :
Wikipedia :
Target
Families : 6_AlphaBeta_hydrolase, Canar_LipB, Hormone-sensitive_lipase_like
Protein : bacsu-cbxnp, canar-LipB, 9delt-EstD11
References (6)
| Title : Crystal structures of two Bacillus carboxylesterases with different enantioselectivities - Rozeboom_2014_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1844_567 |
| Author(s) : Rozeboom HJ , Godinho LF , Nardini M , Quax WJ , Dijkstra BW |
| Ref : Biochimica & Biophysica Acta , 1844 :567 , 2014 |
| Abstract : Rozeboom_2014_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1844_567 |
| ESTHER : Rozeboom_2014_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1844_567 |
| PubMedSearch : Rozeboom_2014_Biochim.Biophys.Acta_1844_567 |
| PubMedID: 24418394 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: bacsu-cbxnp , bacsu-ybfk |
| Title : Immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase on glass beads for enantioselective hydrolysis of racemic naproxen methyl ester - Yilmaz_2011_Bioresour.Technol_102_499 |
| Author(s) : Yilmaz E , Can K , Sezgin M , Yilmaz M |
| Ref : Bioresour Technol , 102 :499 , 2011 |
| Abstract : Yilmaz_2011_Bioresour.Technol_102_499 |
| ESTHER : Yilmaz_2011_Bioresour.Technol_102_499 |
| PubMedSearch : Yilmaz_2011_Bioresour.Technol_102_499 |
| PubMedID: 20846857 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: canru-1lipa |
| Title : Efficient production of (S)-naproxen with (R)-substrate recycling using an overexpressed carboxylesterase BsE-NP01 - Liu_2010_Appl.Biochem.Biotechnol_162_1574 |
| Author(s) : Liu X , Xu JH , Pan J , Zhao J |
| Ref : Appl Biochem Biotechnol , 162 :1574 , 2010 |
| Abstract : Liu_2010_Appl.Biochem.Biotechnol_162_1574 |
| ESTHER : Liu_2010_Appl.Biochem.Biotechnol_162_1574 |
| PubMedSearch : Liu_2010_Appl.Biochem.Biotechnol_162_1574 |
| PubMedID: 20237863 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: bacsu-cbxnp |
| Title : Lipase-catalyzed esterification of (S)-naproxen ethyl ester in supercritical carbon dioxide - Kwon_2009_J.Microbiol.Biotechnol_19_1596 |
| Author(s) : Kwon CH , Lee JH , Kim SW , Kang JW |
| Ref : J Microbiol Biotechnol , 19 :1596 , 2009 |
| Abstract : Kwon_2009_J.Microbiol.Biotechnol_19_1596 |
| ESTHER : Kwon_2009_J.Microbiol.Biotechnol_19_1596 |
| PubMedSearch : Kwon_2009_J.Microbiol.Biotechnol_19_1596 |
| PubMedID: 20075625 |
| Gene_locus related to this paper: canar-LipB |
| Title : Hydrolytic resolution of (R,S)-naproxen 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl thioester by Carica papaya lipase in water-saturated organic solvents - Ng_2005_Biotechnol.Bioeng_89_88 |
| Author(s) : Ng IS , Tsai SW |
| Ref : Biotechnol Bioeng , 89 :88 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Ng_2005_Biotechnol.Bioeng_89_88 |
| ESTHER : Ng_2005_Biotechnol.Bioeng_89_88 |
| PubMedSearch : Ng_2005_Biotechnol.Bioeng_89_88 |
| PubMedID: 15543625 |
| Title : Lipase-catalyzed naproxen methyl ester hydrolysis in water-saturated ionic liquid: significantly enhanced enantioselectivity and stability - Xin_2005_World.J.Microbiol.Biotechnol_21_193 |
| Author(s) : Xin JY , Zhao YJ , Shi YG , Xia CG , Li SB |
| Ref : World J Microbiol Biotechnol , 21 :193 , 2005 |
| Abstract : Xin_2005_World.J.Microbiol.Biotechnol_21_193 |
| ESTHER : Xin_2005_World.J.Microbiol.Biotechnol_21_193 |
| PubMedSearch : Xin_2005_World.J.Microbiol.Biotechnol_21_193 |
| PubMedID: |